Aagya Khatri on Jul 31, 2025
Reading Time: 9 Min
Outsourcing slashes web development costs and accelerates growth, but with significant risks. A 2020 study found 59% of firms hit by data breaches traced them to third-party vendors. However, it was not caused by outsourcing itself, but by weak cyber safeguards in the development pipeline.
A research study by BullGuard found that 23% of SMBs use no device security, 32% rely on free solutions, and most admit to failing to train employees to avoid cyberattacks.
It makes sense for a cybercriminal to target small and medium-sized businesses' cybersecurity, given their potential lapse in security.
The fix is simple: spending more on hiring a reliable outsourcing agency may not be the solution, but ensuring that both parties weave security into every offshore workflow and practice rigorous cyber hygiene to block vulnerabilities, protect their reputation, and build rock-solid digital platforms.
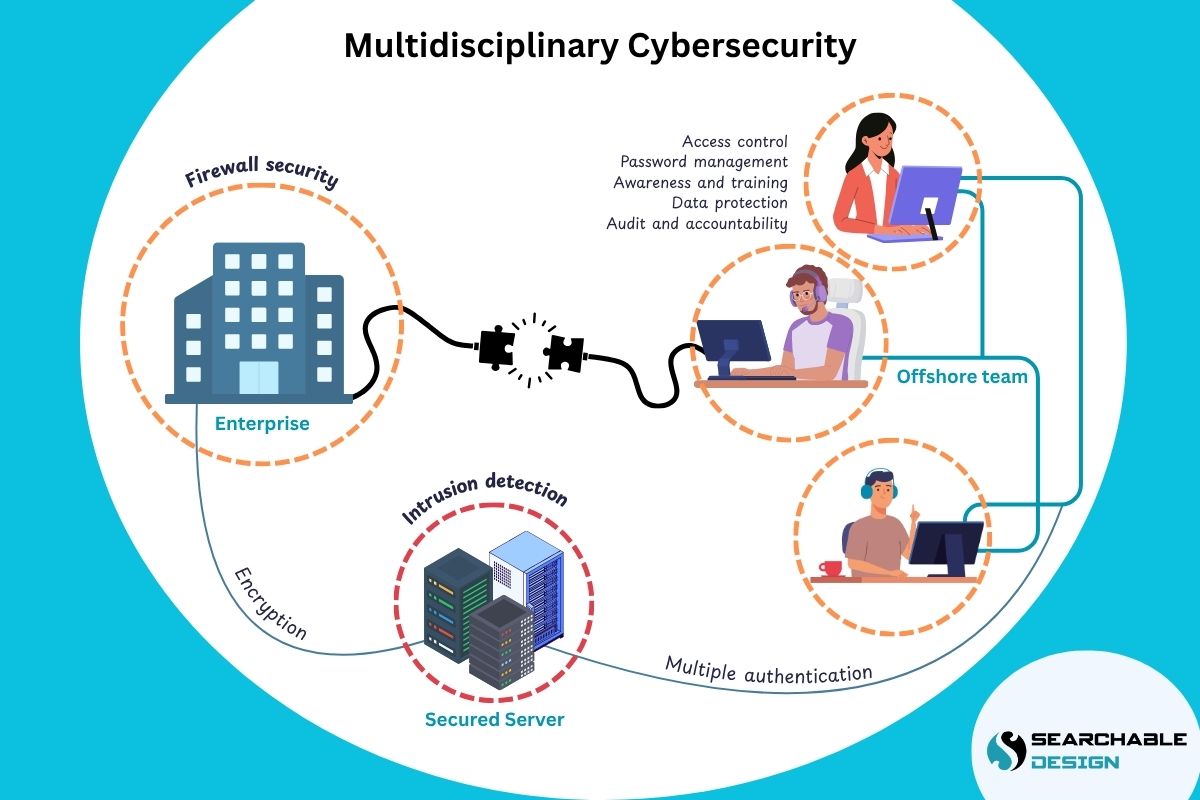
If you are one of the SMBs who have outsourced web development or are about to outsource, then this guide will make a great read.
What is “Cyber Hygiene” in Outsourcing?
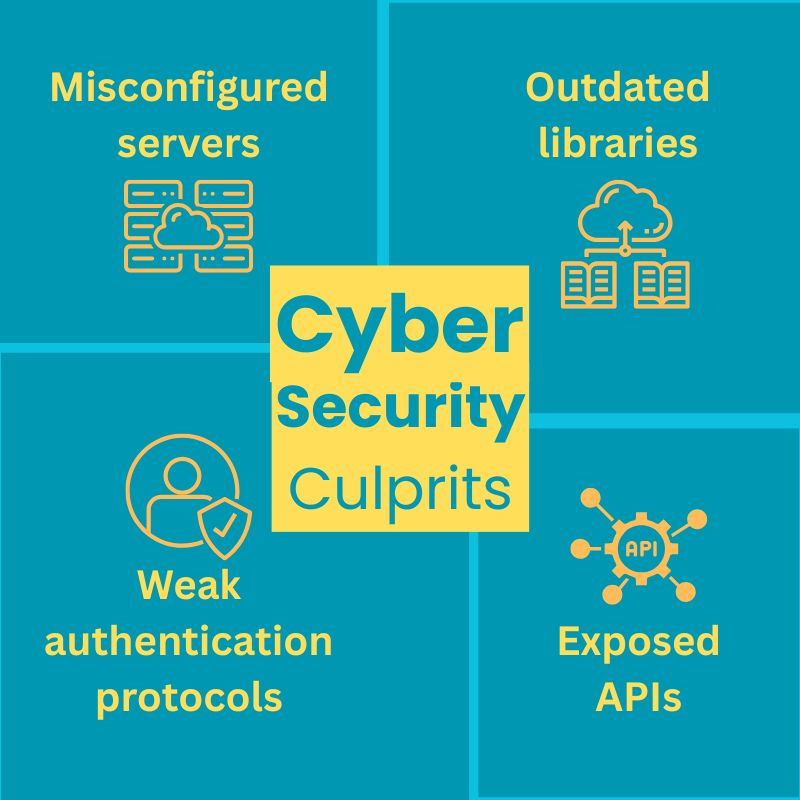
Let’s talk about the culprit first.
Security gaps widen as your code moves across borders, cultures, and legal jurisdictions and creates vulnerabilities like,
“Cyber hygiene” is like good personal hygiene, but for your digital systems. When outsourcing web development, cyber hygiene becomes even more critical because people in different locations across various countries are handling your code and information.
Here is what good cyber hygiene looks like in outsourced web development.
|
Practice |
Key Actions |
Benefit |
|
Secure SDLC |
Build security gates into plan → code → test → deploy |
Catch flaws early; it's cheaper to fix |
|
Vendor Access Control |
Grant contractors least-privilege tool & data access |
Shrinks attack surface |
|
Secure Code Reviews |
Pair review + static-analysis scanners before merge |
Blocks exploitable bugs |
|
Encrypted Communication |
Use VPN, SSH, SFTP, Zero-Trust chat—never plain email |
Keeps credentials & IP safe |
|
Role-Based Authentication |
Map access strictly to job role; audit permissions monthly |
Prevents insider & lateral attacks |
|
Compliance Documentation |
Log evidence of GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA adherence; maintain policy wikis |
Proves due diligence, avoids fines |
Here is what these practices entail.
1. Secure Development Lifecycle (SDLC) for Offshore
Once you have chosen your offshore development team, it is crucial to build cyber hygiene into every step of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC).
Security should never be an alternative; it needs to be part of the plan from day one. Sit down with your security manager, liaison, and offshore project manager to discuss these processes.
|
Process |
Key Actions |
|
Planning |
- Conduct threat modeling by creating risky scenarios. - Define security requirements in project specs. |
|
Development |
- Enforce secure coding standards (e.g., OWASP). - Avoid hardcoded secrets such as API keys, database credentials, and private certificates. - Use static code analysis tools (e.g., SonarQube). |
|
Testing |
- Perform vulnerability assessments and penetration testing. - Use tools like Burp Suite or OWASP ZAP for security scans. |
|
Deployment |
- Set up automated code reviews. - Enforce secure CI/CD pipelines with access controls. - Host on platforms with substantial DDoS mitigation and web application firewalls (WAFs). |
|
Maintenance |
- Apply regular patch updates for software and libraries. - Monitor traffic with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools. - Conduct code audits every two months. |
2. Tips to Choose a Secure Offshore Vendor
Cyber hygiene starts with choosing the right offshore partner. Here is what you need to look for.
a. Security Certifications
Begin by verifying whether the vendor holds recognized security certifications and confirming that they follow global standards and take data protection seriously.
Look for:
- ISO/IEC 27001 – For information security management.
- SOC 2 Type II – Confirms secure handling of client data.
- GDPR compliance – Must-have for businesses with European users.
- HIPAA compliance – Essential for healthcare-related apps.
b. Security-First Culture
Do they train developers on OWASP Top 10? Do they enforce two-factor authentication, VPN usage, and Git access control?
A good vendor,
- Trains developers on the OWASP Top 10 (the most common security risks).
- Enforces two-factor authentication for all accounts.
- Requires VPNs for remote access and controls who can access code on GitHub or GitLab.
c. Infrastructure Hardening
A reliable vendor would not leave systems exposed. They use,
- Hardened servers (servers configured with strict security rules).
- Encrypted devices and endpoints protect all communications.
- Secure CI/CD pipelines that prevent unauthorized code deployment.
d. Contractual Safeguards
Do not skip the paperwork, as it is a fundamental part of the agreement. Your contract should include,
- Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are used to protect your intellectual property.
- Data protection clauses outlining how your data is handled.
- Incident response terms that explain what happens if there is a breach.

3. Secure Code, Communication, and Access
Remote collaboration makes offshore development quick, but it may also open a pathway for cyberattackers to intrude. From source code to team chats, every shared platform becomes a potential risk if not adequately secured.
Over 90% of phishing attacks occur through email or chat tools, where attackers trick users into clicking on unsafe links or sharing their login credentials.
Here is how to do it right.
a. Code Repositories (e.g., GitHub, GitLab)
Your source code is the backbone of your app; protect it like gold.
- Use branch protection rules: Prevent unauthorized changes to main code branches.
- Enforce SAML-based Single Sign-On (SSO): Add a secure login layer across all developer tools.
- Apply role-based access: Junior developers should not have admin-level permissions. Keep access strictly need-based.
b. Project Management Tools (e.g., Jira, Trello)
These tools often hold task notes, comments, and sometimes even sensitive data.
- Never store secrets: Avoid pasting passwords, tokens, or API keys into task descriptions or comments.
- Restrict board access: Ensure sensitive project boards are only visible to the relevant team members.
c. Communication Tools (e.g., Slack, Zoom)
These tools are common phishing targets and must be locked down.
- Use platforms with end-to-end encryption to prevent eavesdropping.
- Disable unnecessary file sharing to prevent potential malware uploads.
- Enable activity logs and bot scanning to quickly detect unusual behavior.
4. Encrypted Communication
When working with offshore teams, a significant amount of sensitive information is shared, including login credentials, project files, database access, and private messages.
If any of this data travels through unsecured channels, such as regular email, it becomes an easy target for hackers.
Encryption ensures that your data is scrambled into unreadable text during transit, and only the proper recipient with the correct key can unlock it. Even if someone intercepts the data, they won’t be able to understand or use it.
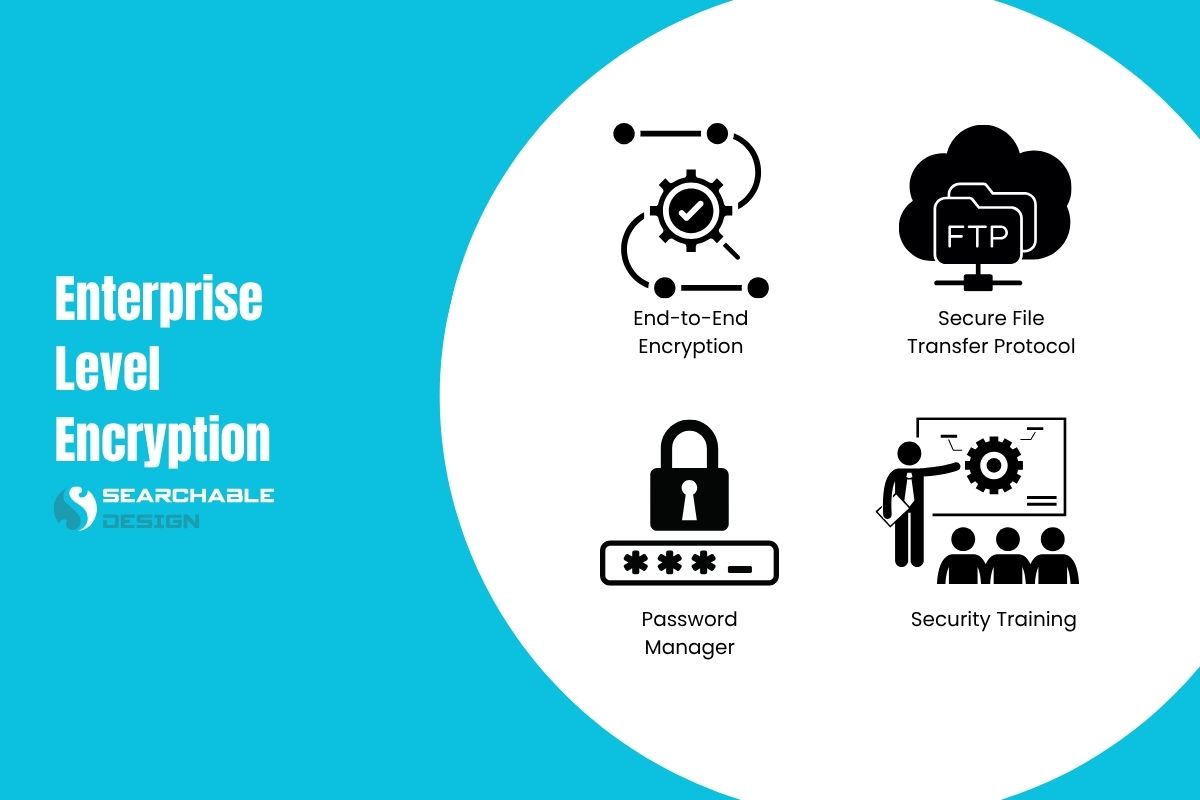
Here’s how to ensure secure communication,
- Never share sensitive information via unsecured email or chat, including Gmail, Outlook, and instant messaging services.
- Use end-to-end encrypted platforms, such as Signal, ProtonMail, or encrypted Slack alternatives to ensure privacy.
- For file transfers, use secure services such as SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol), Google Drive with restricted access, or tools with built-in encryption, like Tresorit.
- Protect credentials with password managers like 1Password or Bitwarden, which securely store and share passwords.
- Enable encryption on video conferencing tools like Zoom or Google Meet, and double-check security settings before meetings.
- Educate team members about phishing attacks and the importance of encrypted sharing.
5. Enforce Least Privilege and Role-Based Access
Access to software, server, and database should be based on the enterprise role. The more people who can access sensitive systems, the greater the chances are for mistakes or breaches.
Grant each team member only the minimum access necessary to perform their job. For example, a front-end developer doesn’t need access to your database or server configuration.
Here is how to enforce access control smartly.
- Role-based permissions: Define user roles (developer, designer, tester, admin) and assign access accordingly.
- Use IAM tools: Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools, such as AWS IAM, Azure AD, or Okta, help manage permissions centrally.
- Audit access regularly: Review who has access monthly and remove users who no longer require it.
- Use temporary access tokens: For special tasks, grant time-limited access that automatically expires.
- Enable MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication): Add an extra layer of security for all users, especially those with sensitive permissions.
6. Legal, Compliance, and Data Privacy Considerations
Even if your systems are secure, you can still get into legal trouble if your offshore team does not follow data protection laws.
These laws protect users’ personal information, such as names, emails, and browsing habits, and they vary from country to country.
Here are some major data privacy laws your vendor should know,
- GDPR (Europe): It protects the personal data of anyone in the European Union. Users have the right to understand how their data is used, to delete it, or to say “no” to tracking.
- CCPA (California): It grants individuals in California the right to view, delete, or opt out of the sale of their data.
- PDPA (Singapore and other parts of Asia): It ensures that personal data is collected and used fairly, with the individual's consent.
- DPDPA (India): It focuses on protecting digital personal data. Vendors must process data only with explicit permission and secure it properly.
Key Takeaways for Secure Web-Development Outsourcing
Let us revise all the crucial insights into a few takeaway points.
- Vet the Vendor, Not Just the Price: Check security certifications (ISO 27001, SOC 2), past breaches, and client references.
- Bake Security Into the Contract: Include NDAs, IP-ownership clauses, SLAs for vulnerability fixes, and right-to-audit provisions.
- Insist on a Secure SDLC: Require threat modeling, static/dynamic code scans, and security gates at every stage.
- Apply Least-Privilege Access: Grant external devs only the repositories, servers, and data they need—nothing more.
- Encrypt Everything in Motion & at Rest: Use VPN/SSH for remote access, SFTP for file transfer, and encrypted vaults for credentials.
- Mandate Dual Code Reviews: Combine human peer review with automated scanning to catch logic flaws and OWASP top-10 issues.
- Enforce Role-Based Authentication & MFA: Tie permissions to job roles and add multi-factor authentication for all privileged accounts.
- Track Compliance & Documentation: Log data flows, store audit trails, and verify adherence to GDPR, HIPAA, or regional equivalents.
- Run Regular Pen Tests & Third-Party Audits: Schedule external penetration tests and require vendors to remediate any findings promptly.
- Have an Incident-Response Playbook: Define who is responsible for what, when, and how in the event of a breach; rehearse it at least annually.
Conclusion
In a world where data is currency and breaches are akin to bankruptcies, embedding cyber hygiene in offshore pipelines is a necessity.
Whether you are a startup founder or an enterprise CTO, it is your responsibility to transform offshore partnerships into secure digital ecosystems.
To integrate the right workforce, tools, mindset, and processes in your business, contact Searchable Design, the best outsourcing partner in the US.
Comments(0)
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Recommended Posts
Unlock the Secret of Power BI to Empower Your Data Analysis
Turn Raw Data into Real-Time Intelligence with Power BI
Why More Startups Are Offshoring Data Engineering Roles in 2025
Unlocking Global Talent for Faster, Smarter, Scalable Growth through Offshoring Data Engineering
How to Empower Your Web Development Project in 2025?
Empowering Your Web Build with the Right Strategy, Stack, and Global Talent Network
RECOMMENDED TOPICS
TAGS
- offshoring
- outsourcing
- web development
- data analytics
- artificial intelligence
- offshore
- it support
- digital marketing
- project management
- agile methodology
- project management system
- data
- pms
- data centric approach
- app development
- customer insight
- it infrastructure
- it sustainability
- cloud computing
- agentic ai
- business process automation
- voice search optimization
- seo
- tiktok
- growth hack
- saas
- data engineering
- global talent pool
- techical consulting
- power bi
- business intelligence
- backoffice
- communication
- outsource
- remote team
- it roles
- web security
- data engineer
- content development
- business development
- offshore talent
- legacy software
- insurtech
- insurance
- off
- data decision
- test
About
Data Not Found
NEWSLETTER
Related Posts
How to Empower Your Web Development Project in 2025?
Empowering Your Web Build with the Right Strategy, Stack, and Global Talent Network
Benefits of Technical Consulting in Professional Marketing Strategy
Bridging Innovation and Strategy for Unstoppable Growth